Spectrum Sharing between Radar and Communication Systems
1
Sponsors:
Problem Statement and Motivation
- Increased demand for wireless services necessitates the spectrum co-existence between radar and communication systems.
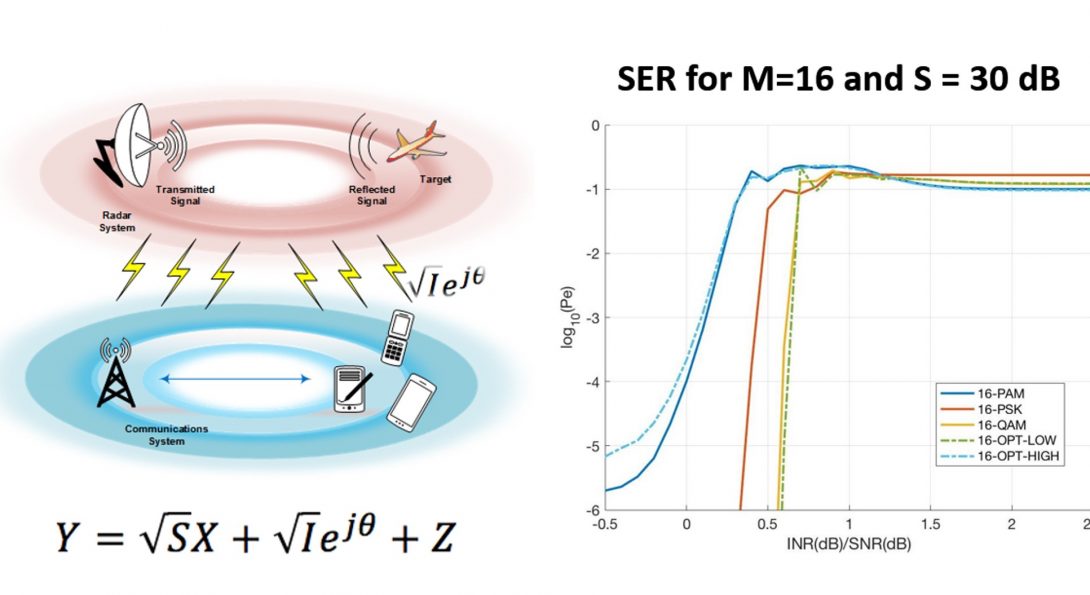
- How an unaltered radar pulse affects the performance of an uncoded communication RX in terms of the Symbol Error Rate (SER).
- Optimize a signal constellation that achieves lowest SER:
- Weak radar interference (INR << SNR):
- Radar interference is treated as Gaussian noise.
- Optimal constellation has a shape of concentric hexagons.
- Moderate radar interference (INR ≈ SNR):
- Yields the highest SER.
- Strong radar interference (INR >> SNR >> 1):
- Radar signal is completely canceled along with part of comm signal resulting in an irreducible error floor.
- Optimal constellation has a shape of an unevenly-spaced PAM.
- Weak radar interference (INR << SNR):
Technical Approach
- Derive the SER for the optimal ML decoder and its approximations using the communication theoretic approach.

Key Achievements and Future Goals
- N. Nartasilpa, D. Tuninetti, N. Devroye, and D. Erricolo, “Let’s share CommRad: effect of radar interference on an uncoded data commu- nication system,” in Proc. of IEEE RadarCon, May 2016.
- N. Nartasilpa, D. Tuninetti, N. Devroye, and D. Erricolo, “On the error rate of a communication system suffering from additive radar interfer- ence,” in Proc. of IEEE GlobeCom, Dec 2016.
- N. Nartasilpa, D. Tuninetti, N. Devroye, and D. Erricolo, “Signal constellation optimization in the presence of radar interference and Gaussian noise,” in submitted to Proc. of IEEE ICC, May 2017.
- Extensions to more practical models such as fading channels, OFDM channels, MIMO channels, and channel-coded systems.


